Last Updated on 29/11/2025 by Eran Feit
This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide on how to implement and train a UNet Tensorflow model for Melanoma detection using TensorFlow and Keras.
🔍 What You’ll Learn 🔍:
Building U-net model : Learn how to construct the model using TensorFlow and U-net Keras.
Unet Tensorflow Model Training: We’ll guide you through the training process, optimizing your model to generate masks in the lungs position
Testing and Evaluation: Run the pre-trained model on a new fresh images , and visual the test image next to the predicted mask .
Check out our tutorial here : https://youtu.be/-AejMcdeOOM?si=JibmFeIoXPaiVVZC
Link for the full code here : https://eranfeit.lemonsqueezy.com/buy/33b5c656-1272-4429-95c8-a81354569c7f or here: https://ko-fi.com/s/3f1fdb4316
You can find more tutorials, and join my newsletter here : https://eranfeit.net/
This tutorial is based on the U-net Architecture :
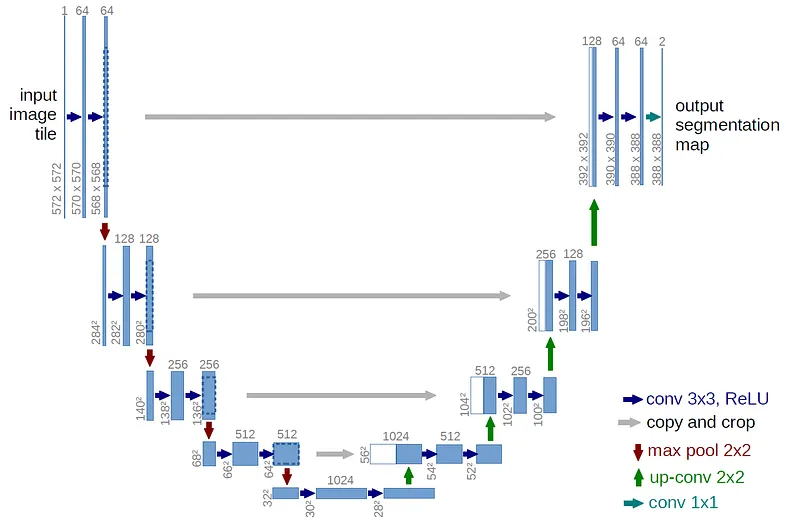
Here is the code for segment X-Ray lungs using U-net and Tensorflow :
Dataset name – Academic Montgomery County X-ray Set
You can download the dataset here : https://academictorrents.com/details/ac786f74878a5775c81d490b23842fd4736bfe33
Part 1 : Dataset loading and Preprocessing :
This code processes the Montgomery County X-ray Dataset, which contains chest X-rays and their corresponding lung segmentation masks (left and right lungs separately).
The code loads these images, preprocesses them, and prepares them for training a segmentation Unet Tensorflow model. It performs tasks like resizing images, normalizing pixel values, combining left and right lung masks, and splitting the data into training and validation sets.
# Import required libraries import cv2 # OpenCV library for image processing import numpy as np # NumPy for numerical operations import glob # For finding files matching a pattern from tqdm import tqdm # For displaying progress bars # Define image dimensions for resizing Height = 256 Width = 256 # Define file paths for images and masks path = "E:/Data-sets/Lung Segmentation/MontgomerySet/" imagesPath = path + "CXR_png/*.png" # Path to X-ray images leftMaskPath = path + "ManualMask/leftMask/*.png" # Path to left lung masks rightMaskPath = path + "ManualMask/rightMask/*.png" # Path to right lung masks # Get lists of all image files using glob print ("Images in folder , left mask images , right mask images :") listOfImages = glob.glob(imagesPath) # Get list of X-ray images listOfLeftMaskImages = glob.glob(leftMaskPath) # Get list of left mask images listOfRightMaskImages = glob.glob(rightMaskPath) # Get list of right mask images # Print number of images found in each category print(len(listOfImages)) print(len(listOfLeftMaskImages)) print(len(listOfRightMaskImages)) # Load and display a sample image and its masks img = cv2.imread(listOfImages[0], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # Read first X-ray image print(img.shape) # Print original image dimensions # Resize X-ray image to target dimensions img = cv2.resize(img , (Width, Height)) # Load left and right lung masks for the first image left_mask = cv2.imread(listOfLeftMaskImages[0], cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) right_mask = cv2.imread(listOfRightMaskImages[0], cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) # Resize both masks to target dimensions left_mask = cv2.resize(left_mask , (Width, Height)) right_mask = cv2.resize(right_mask , (Width, Height)) # Combine left and right masks into a single mask finalMask = left_mask + right_mask # Display the images and masks cv2.imshow("img", img) cv2.imshow("left_mask", left_mask) cv2.imshow("right_mask", right_mask) cv2.imshow("finalMask", finalMask) cv2.waitKey(0) # Wait for key press before continuing # Demonstrate mask value processing mask16 = cv2.resize(left_mask, (16,16)) # Resize mask to smaller dimensions for demonstration print(mask16) # Print original mask values # Convert mask values to binary (0 and 1) mask16[mask16 > 0 ] = 1 print("======================================") print(mask16) # Print binary mask values # Initialize empty lists for storing processed images and masks allImages = [] maskImages = [] # Process all images and masks print("start loading the train images and masks + images augmentation X3") for imgFile , leftMask, rightMask in tqdm(zip(listOfImages, listOfLeftMaskImages, listOfRightMaskImages), total = len(listOfImages)): # Load and preprocess X-ray image img = cv2.imread(imgFile, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) img = cv2.resize(img, (Width, Height)) # Resize image img = img / 255.0 # Normalize pixel values to range [0,1] img = img.astype(np.float32) # Convert to float32 allImages.append(img) # Load and process mask images leftMask = cv2.imread(leftMask, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) rightMask = cv2.imread(rightMask, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) mask = leftMask + rightMask # Combine masks mask = cv2.resize(mask, (Width, Height)) # Resize mask mask[mask>0] = 1 # Convert to binary mask maskImages.append(mask) # Convert lists to NumPy arrays allImagesNP = np.array(allImages) maskImagesNP = np.array(maskImages) maskImagesNP = maskImagesNP.astype(int) # Convert masks to integer type # Print shapes of processed data print("Shapes of train images and masks :") print(allImagesNP.shape) print(maskImagesNP.shape) # Split data into training and validation sets from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split split = 0.1 # 10% validation split # Perform train-test split train_imgs, valid_imgs = train_test_split(allImagesNP, test_size=split , random_state=42) train_masks, valid_masks = train_test_split(maskImagesNP, test_size=split, random_state=42) # Print shapes of training and validation sets print("Shapes of train images and masks : ") print(train_imgs.shape) print(train_masks.shape) print("Shapes of Validat images and masks : ") print(valid_imgs.shape) print(valid_masks.shape) # Save processed data to NumPy files print("Save the data :") np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Lung-Images.npy", train_imgs) np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Lung-Masks.npy", train_masks) np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Validate-Lung-Images.npy", valid_imgs) np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Validate-Lung-Masks.npy", valid_masks) print("Finish save the data")Link for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/3f1fdb4316
Part 2 : The Unet Tensoflow model (Save it as “Step02Model.py”) :
This code implements a U-Net Keras model using TensorFlow and Keras. U-Net is a popular architecture for image segmentation tasks, with an encoder-decoder structure and skip connections. The model takes an input image and produces a segmentation mask. The architecture consists of a convolutional block helper function and the main model-building function.
This code defines a U-Net architecture with:
- An encoder path that reduces spatial dimensions while increasing feature channels
- A bridge section at the bottom with the highest number of filters
- A decoder path that increases spatial dimensions while decreasing feature channels
- Skip connections that connect corresponding encoder and decoder levels
- A final output layer that produces a binary segmentation mask
The Unet Tensorflow model is particularly effective for medical image segmentation tasks, like the lung segmentation task it’s being used for here.
Key features:
- Uses repeated blocks of Conv2D, BatchNormalization, and ReLU activation
- Implements skip connections to preserve spatial information
- Uses max pooling for downsampling and upsampling for decoder path
- Produces a binary segmentation mask through sigmoid activation
- Follows the classic U-Net architecture pattern of contracting and expanding paths
# Import required TensorFlow and Keras libraries import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.layers import * # Import all Keras layers from tensorflow.keras.models import Model # Import Keras Model class # Define a convolutional block function that will be used throughout the network def conv_block(x, num_filters): # First convolutional layer x = Conv2D(num_filters, (3,3), padding="same")(x) # Apply 3x3 convolution x = BatchNormalization()(x) # Normalize the activations x = Activation("relu")(x) # Apply ReLU activation function # Second convolutional layer x = Conv2D(num_filters, (3,3), padding="same")(x) # Apply another 3x3 convolution x = BatchNormalization()(x) # Normalize the activations x = Activation("relu")(x) # Apply ReLU activation function return x # Define the main U-Net model building function def build_model(shape): # Define the number of filters for each level of the network num_filters = [64,128,256,512] # Filters double at each level # Create the input layer with specified shape inputs = Input((shape)) # List to store skip connections skip_x = [] x = inputs # Encoder path (Contracting path) for f in num_filters: x = conv_block(x,f) # Apply convolution block skip_x.append(x) # Store the output for skip connection x = MaxPool2D((2,2))(x) # Apply max pooling to reduce dimensions # Bridge (Bottom of the U) x = conv_block(x, 1024) # Apply convolution block with 1024 filters # Reverse the filter list and skip connections for the decoder path num_filters.reverse() # Reverse filter order for decoder skip_x.reverse() # Reverse skip connections order # Decoder path (Expanding path) for i, f in enumerate(num_filters): x = UpSampling2D((2,2))(x) # Upsample the feature map xs = skip_x[i] # Get corresponding skip connection x = Concatenate()([x,xs]) # Concatenate with skip connection x = conv_block(x,f) # Apply convolution block # Output layer x = Conv2D(1, (1,1), padding="same")(x) # 1x1 convolution to get final output x = Activation("sigmoid")(x) # Sigmoid activation for binary segmentation # Create and return the model return Model(inputs, x)Link for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/3f1fdb4316
Part 3 : Train the Unet Tensorflow model :
This script loads preprocessed image data for training and validating a U-Net Keras model for lung segmentation.
It sets up a Unet TensorFlow based deep learning model, compiles it with an Adam optimizer and binary cross-entropy loss, and trains it using predefined hyperparameters while applying model checkpointing, learning rate reduction, and early stopping callbacks.
import numpy as np ### Import NumPy, a library for numerical computing, which is used for handling arrays. # load the data ### Print a message indicating the start of data loading. print("start lodaing ") ### Load the training images from a `.npy` file. allImagesNp = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Lung-Images.npy") ### Load the corresponding masks (segmentation labels) for training images. maskImagesNp = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Lung-Masks.npy") ### Load the validation images. allValidateImagesNP = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Validate-Lung-Images.npy") ### Load the validation masks. maskValidateImagesNP = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Validate-Lung-Masks.npy") ### Print the shapes of the loaded datasets to verify correct dimensions. print(allImagesNp.shape) print(maskImagesNp.shape) print(allValidateImagesNP.shape) print(maskValidateImagesNP.shape) ### Define the height and width of the input images. Height = 256 Width = 256 # build the model ### Import TensorFlow and necessary Keras utilities for defining and training the model. import tensorflow as tf ### Import `build_model` function from `Step02Model` to construct the U-Net model. from Step02Model import build_model ### Import Keras callbacks for saving the best model, adjusting learning rate, and stopping early. from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping ### Define the input shape (256x256 with 3 color channels), learning rate, batch size, and epochs. shape = (256, 256, 3) lr = 1e-4 # 0.0001 batchSize = 4 epochs = 50 ### Build the U-Net model. model = build_model(shape) ### Print the model architecture summary. print(model.summary()) ### Use the Adam optimizer with the defined learning rate. opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr) ### Compile the model with binary cross-entropy loss and accuracy as a metric. model.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=opt, metrics=['accuracy']) ### Compute the number of steps per epoch for training and validation. stepsPerEpoch = np.ceil(len(allImagesNp) / batchSize) validationSteps = np.ceil(len(allValidateImagesNP) / batchSize) ### Define the file path where the best model will be saved. best_model_file = "e:/temp/lung-Unet.h5" ### Set up callbacks: ### - Save the best model based on validation loss. ### - Reduce the learning rate if validation loss does not improve for 5 epochs. ### - Stop training if validation accuracy does not improve for 20 epochs. callbacks = [ ModelCheckpoint(best_model_file, verbose=1, save_best_only=True), ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor="val_loss", patience=5, factor=0.1, verbose=1, min_lr=1e-7), EarlyStopping(monitor="val_accuracy", patience=20, verbose=1) ] ### Train the model using the loaded data. ### Use mini-batches, shuffle data, validate after each epoch, and apply callbacks. history = model.fit( allImagesNp, maskImagesNp, batch_size=batchSize, epochs=epochs, verbose=1, validation_data=(allValidateImagesNP, maskValidateImagesNP), validation_steps=validationSteps, steps_per_epoch=stepsPerEpoch, shuffle=True, callbacks=callbacks )Link for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/3f1fdb4316
Part 4 : Test the Unet Tensorflow model (inference) :
This script loads a pre-trained U-Net Keras model for lung segmentation, processes a test image, predicts the segmented lung region, and displays both the original image and the predicted mask.
It resizes the image, normalizes pixel values, applies a binary threshold to the mask, and visualizes the results using OpenCV.
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import cv2 ### Import necessary libraries: ### - NumPy for handling arrays. ### - TensorFlow for loading the trained model and making predictions. ### - OpenCV for image processing. # load the saved model ### Define the path to the best saved model. best_model_file = "e:/temp/lung-Unet.h5" ### Load the pre-trained U-Net model from the specified file. model = tf.keras.models.load_model(best_model_file) ### Print the model architecture summary. print(model.summary()) ### Define the width and height of the input image for resizing. Width = 256 Height = 256 # load test image ### Define the path to the test image. testImagePath = "TensorFlowProjects/Unet-Projects/Lung Segmentation/Lung-test-Image-From-Google.jpeg" ### Read the test image using OpenCV. img = cv2.imread(testImagePath) ### Resize the image to match the input size expected by the model. img2 = cv2.resize(img, (Width, Height)) ### Normalize the pixel values by dividing by 255 (scaling to the range [0,1]). img2 = img2 / 255.0 ### Expand dimensions to match the model's input shape (batch size of 1). imgForModel = np.expand_dims(img2, axis=0) ### Perform prediction using the trained model. p = model.predict(imgForModel) ### Extract the predicted segmentation mask. resultMask = p[0] ### Print the shape of the predicted mask to verify dimensions. print(resultMask.shape) # Process the prediction output ### Since this is a binary segmentation task: ### - Any value below or equal to 0.5 is set to 0 (black, no object detected). ### - Any value above 0.5 is set to 255 (white, object detected). resultMask[resultMask <= 0.5] = 0 resultMask[resultMask > 0.5] = 255 ### Define the scaling percentage for displaying images. scale_precent = 60 # Resize factor for display purposes. ### Compute the new width and height based on the scale percentage. w = int(img.shape[1] * scale_precent / 100) h = int(img.shape[0] * scale_precent / 100) ### Define the new image dimensions. dim = (w, h) ### Resize the original image for display. img = cv2.resize(img, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) ### Resize the predicted mask for display. mask = cv2.resize(resultMask, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) ### Display the original test image. cv2.imshow("first image", img) ### Display the predicted segmentation mask. cv2.imshow("Predicted mask", mask) ### Wait for a key press to close the displayed images. cv2.waitKey(0)Link for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/3f1fdb4316
The Unet Tensorflow result :
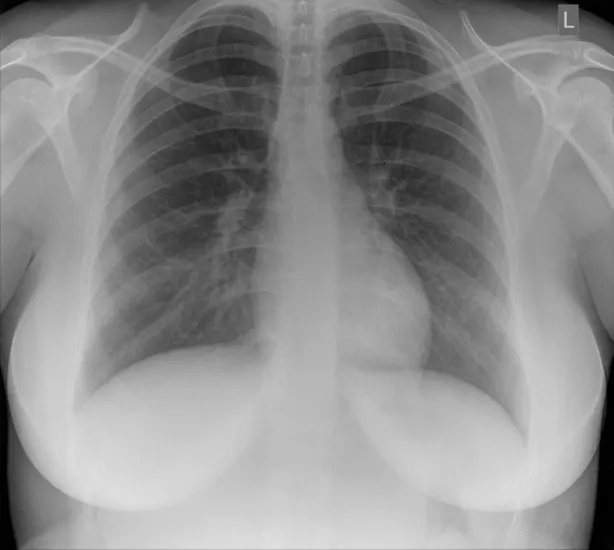
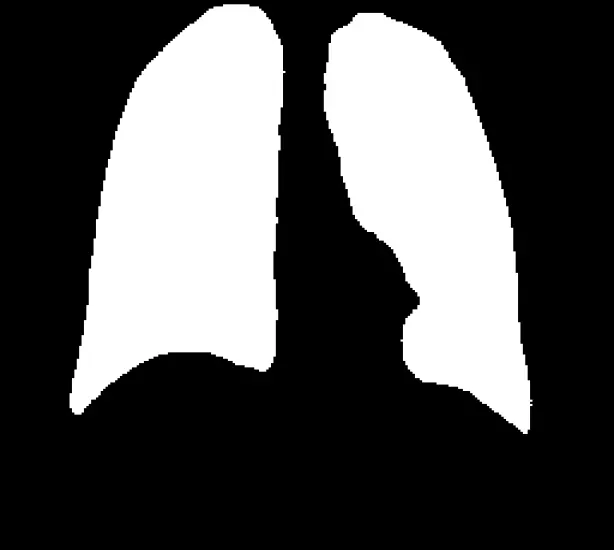
Connect :
☕ Buy me a coffee — https://ko-fi.com/eranfeit
🖥️ Email : feitgemel@gmail.com
🤝 Fiverr : https://www.fiverr.com/s/mB3Pbb
Planning a trip and want ideas you can copy fast?
Here are three detailed guides from our travels:
• 5-Day Ireland Itinerary: Cliffs, Castles, Pubs & Wild Atlantic Views
https://eranfeit.net/unforgettable-trip-to-ireland-full-itinerary/
• My Kraków Travel Guide: Best Places to Eat, Stay & Explore
https://eranfeit.net/my-krakow-travel-guide-best-places-to-eat-stay-explore/
• Northern Greece: Athens, Meteora, Tzoumerka, Ioannina & Nafpaktos (7 Days)
https://eranfeit.net/my-amazing-trip-to-greece/
Each guide includes maps, practical tips, and family-friendly stops—so you can plan in minutes, not hours.
Enjoy,
Eran
