Last Updated on 14/02/2026 by Eran Feit
TensorFlow U-Net melanoma segmentation is a computer-vision workflow where the model predicts a pixel mask of the lesion area (segmentation), not a medical diagnosis.
In this tutorial, you’ll train a classic U-Net in TensorFlow/Keras on the ISIC 2018 skin-lesion dataset and run inference to visualize predicted masks on new images.
You’ll see the full pipeline: dataset structure, preprocessing + augmentation, model training, and practical inference/visualization steps so you can reproduce results on your own machine.
Important (read first): This post is for educational and research purposes only. It is not medical advice and is not a diagnostic tool. If you have a medical concern, consult a qualified clinician.

This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide on how to implement and train a U-Net model for Melanoma detection using TensorFlow/Keras.
🔍 What You’ll Learn 🔍:
Data Preparation: We’ll begin by showing you how to access and preprocess a substantial dataset of Melanoma images and corresponding masks.
Data Augmentation: Discover the techniques to augment your dataset. It will increase and improve your model’s results Model Building: Build a U-Net, and learn how to construct the model using TensorFlow and Keras.
Model Training: We’ll guide you through the training process, optimizing your Melanoma Detection model to distinguish Melanoma from non-Melanoma skin lesions.
Testing and Evaluation: Run the pre-trained model on a new fresh images . Explore how to generate masks that highlight Melanoma regions within the images.
Visualizing Results: See the results in real-time as we compare predicted masks with actual ground truth masks.
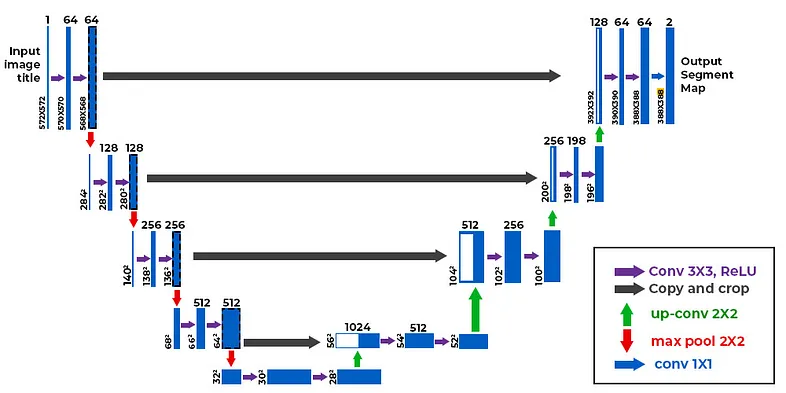
This tutorial is based on the U-net Architecture :
U-Net is an encoder–decoder segmentation architecture designed to predict a pixel-level mask rather than a single class label. The encoder (downsampling path) gradually reduces spatial resolution while increasing feature depth, so the network learns higher-level context like “where the lesion is” and broader shape cues. The decoder (upsampling path) then restores resolution step by step, turning those learned features back into a full-size mask that aligns with the original image.
What makes U-Net especially strong for medical images is the set of skip connections between matching encoder and decoder stages. These connections pass high-resolution details (edges, fine boundaries, texture) directly to the decoder, helping it recover sharp borders instead of producing blurry masks. In practice, this means the model can combine global context (overall lesion location/shape) with local detail (precise contour), which is exactly what you need when segmenting lesions where boundary accuracy matters.
Here is the code for Medical Melanoma Detection :
Download The dataset :
Search in Google : “ISIC Challenge Datasets 2018” and go to 2018 tab
Dataset : https://challenge.isic-archive.com/data/#2018
2594 images and 12970 corresponding ground truth response masks (5 for each image)
Size : 10.5 Giga
Dataset and Folder Structure (ISIC 2018)
This project uses the ISIC 2018 challenge images and masks, which is a common benchmark for skin-lesion segmentation.
Before running the code, confirm you can load an image and its matching mask and that both resize correctly to your chosen input size.
A small setup detail that saves hours: keep your dataset folders clean and consistent (train/test images and train/test masks). Most “model doesn’t learn” issues come from mismatched filenames, mask formats, or resizing that breaks alignment.
What the Preprocessing and Augmentation Actually Do
The preprocessing stage standardizes your input: resizing to a fixed resolution and normalizing pixel values so training is stable.
Then augmentation (flip/rotate) increases variety so the model doesn’t memorize a small set of lesion shapes or lighting conditions.
When segmentation results look “blurry” or shifted, it’s usually an augmentation alignment issue (image transformed but mask not transformed identically). That’s why it’s worth visually inspecting a few augmented image+mask pairs early.
Extra info (Download the code , Newsletter signup …. ) :
Check out our tutorial here: https://youtu.be/P7DnY0Prb2U
Part 1 : Dataset Preprocessing and Augmentation Pipeline
Before we continue , I actually recommend this book for deep learning based on Tensorflow and Keras : https://amzn.to/3STWZ2N
Link for Medium users here .
You can find more tutorials, and join my newsletter here : https://eranfeit.net/
Link for the full code here : https://eranfeit.lemonsqueezy.com/buy/4cd01a4b-ca1a-408f-96f8-fcef84b71f93 or here : https://ko-fi.com/s/901f79116c
# Title: ISIC Dataset Preprocessing and Augmentation Pipeline # Description: # This script processes and augments the ISIC 2018 dataset for melanoma segmentation tasks. # It performs data preprocessing, such as resizing and normalization, and applies augmentations # like flipping and rotation to expand the dataset. The resulting training and testing datasets # are saved as NumPy arrays for further use in deep learning models. # Part 1: Import libraries and set global parameters # Importing necessary libraries for image processing, numerical computation, and data handling. import cv2 # For image processing import numpy as np # For numerical operations and data handling import pandas as pd # For handling tabular data (unused here but common in pipelines) import glob # For file path pattern matching from tqdm import tqdm # For displaying progress bars during loops # Set global parameters for image dimensions Height = 128 # Target height for resizing images Width = 128 # Target width for resizing images # Define paths for datasets path = "E:/Data-sets/Melanoma/" # Base directory for the dataset imagesPath = path + "ISIC2018_Task1-2_Training_Input/*.jpg" # Path for training images maskPath = path + "ISIC2018_Task1_Training_GroundTruth/*.png" # Path for ground truth masks # Part 2: Display the number of images and masks in the folder # Using glob to find the total number of image and mask files print("Images in folder :") listofImages = glob.glob(imagesPath) # List of all image files matching the path pattern print(len(listofImages)) # Print the number of images listOfMasks = glob.glob(maskPath) # List of all mask files matching the path pattern print(len(listOfMasks)) # Print the number of masks # Part 3: Load one image and one mask for inspection # Load and resize a sample image and its corresponding mask img = cv2.imread(listofImages[0], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # Load the first image in color mode print(img.shape) # Print the original dimensions of the image img = cv2.resize(img, (Width, Height)) # Resize the image to predefined dimensions mask = cv2.imread(listOfMasks[0], cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) # Load the corresponding mask in grayscale mode mask = cv2.resize(mask, (Width, Height)) # Resize the mask to match the image dimensions # Part 4: Perform augmentation on the sample image # Apply horizontal flip, vertical flip, and rotation to the sample image import imgaug as ia # Library for image augmentation import imgaug.augmenters as iaa # Augmentation functions hflip = iaa.Fliplr(p=1.0) # Horizontal flip with 100% probability hflipImg = hflip.augment_image(img) # Apply horizontal flip to the image vflip = iaa.Flipud(p=1.0) # Vertical flip with 100% probability vflipImg = vflip.augment_image(img) # Apply vertical flip to the image rot1 = iaa.Affine(rotate=(-50, 20)) # Random rotation between -50 and 20 degrees rotImg = rot1.augment_image(img) # Apply rotation to the image # Display the augmented images cv2.imshow("hflipImg", hflipImg) # Display the horizontally flipped image cv2.imshow("vflipImg", vflipImg) # Display the vertically flipped image cv2.imshow("rotImg", rotImg) # Display the rotated image # Part 5: Investigate the mask # Resize the mask to a smaller size to examine its values mask16 = cv2.resize(mask, (16, 16)) # Downscale the mask to 16x16 for easier inspection print(mask16) # Print the values of the resized mask # Convert mask values: 0 for background, 255 for objects, to binary (0 and 1) mask16[mask16 > 0] = 1 # Set all non-zero values to 1 print("================================== New mask ") print(mask16) # Print the binary mask # Display the original image and mask cv2.imshow("img", img) # Show the original resized image cv2.imshow("mask", mask) # Show the resized mask cv2.waitKey(0) # Wait for a key press before closing the displayed images # Part 6: Load all training images and masks # Initialize lists to store images and masks allImages = [] # List to hold all preprocessed images maskImages = [] # List to hold all preprocessed masks print(len(listofImages)) # Print the total number of images print(len(listOfMasks)) # Print the total number of masks print("Start loading the train images and masks, and augment each image in 3 types") # Loop through all images and masks, apply resizing, normalization, and augmentation for imgFile, imgMask in tqdm(zip(listofImages, listOfMasks), total=len(listofImages)): # Load and preprocess the image img = cv2.imread(imgFile, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # Load image in color mode img = cv2.resize(img, (Width, Height)) # Resize image to match target dimensions img = img / 255.0 # Normalize pixel values to [0, 1] img = img.astype(np.float32) # Convert to float32 type allImages.append(img) # Add preprocessed image to the list # Load and preprocess the mask mask = cv2.imread(imgMask, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) # Load mask in grayscale mode mask = cv2.resize(mask, (Width, Height)) # Resize mask to match target dimensions mask[mask > 0] = 1 # Convert mask to binary values (0 or 1) maskImages.append(mask) # Add preprocessed mask to the list # Apply augmentation and store results hflip = iaa.Fliplr(p=1.0) # Horizontal flip hflipImg = hflip.augment_image(img) # Augmented image hflipMask = hflip.augment_image(mask) # Augmented mask allImages.append(hflipImg) maskImages.append(hflipMask) vflip = iaa.Flipud(p=1.0) # Vertical flip vflipImg = vflip.augment_image(img) vflipMask = vflip.augment_image(mask) allImages.append(vflipImg) maskImages.append(vflipMask) rot1 = iaa.Affine(rotate=(-50, 20)) # Random rotation rotImg = rot1.augment_image(img) rotMask = rot1.augment_image(mask) allImages.append(rotImg) maskImages.append(rotMask) # Convert lists to NumPy arrays for efficient processing allImagesNP = np.array(allImages) # Convert images list to NumPy array maskImagesNP = np.array(maskImages) # Convert masks list to NumPy array maskImagesNP = maskImagesNP.astype(int) # Ensure mask values are integers print("Shapes of train Images and masks") print(allImagesNP.shape) # Print shape of the images array print(maskImagesNP.shape) # Print shape of the masks array # Part 7: Load and preprocess test images and masks # Similar processing steps for test data imagesPath = path + "ISIC2018_Task1-2_Test_Input/*.jpg" # Path for test images maskPath = path + "ISIC2018_Task1_Test_GroundTruth/*.png" # Path for test masks allTestImages = [] # List to hold test images maskTestImages = [] # List to hold test masks print("Images in folder :") listofImages = glob.glob(imagesPath) # Get list of test images print(len(listofImages)) # Print the number of test images listOfMasks = glob.glob(maskPath) # Get list of test masks print(len(listOfMasks)) # Print the number of test masks print("Start loading the Test images and masks, and augment each image in 3 types") for imgFile, imgMask in tqdm(zip(listofImages, listOfMasks), total=len(listofImages)): # Load and preprocess the image img = cv2.imread(imgFile, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) img = cv2.resize(img, (Width, Height)) img = img / 255.0 img = img.astype(np.float32) allTestImages.append(img) # Load and preprocess the mask mask = cv2.imread(imgMask, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) mask = cv2.resize(mask, (Width, Height)) mask[mask > 0] = 1 maskTestImages.append(mask) # Apply augmentation and store results hflip = iaa.Fliplr(p=1.0) hflipImg = hflip.augment_image(img) hflipMask = hflip.augment_image(mask) allTestImages.append(hflipImg) maskTestImages.append(hflipMask) vflip = iaa.Flipud(p=1.0) vflipImg = vflip.augment_image(img) vflipMask = vflip.augment_image(mask) allTestImages.append(vflipImg) maskTestImages.append(vflipMask) rot1 = iaa.Affine(rotate=(-50, 20)) rotImg = rot1.augment_image(img) rotMask = rot1.augment_image(mask) allTestImages.append(rotImg) maskTestImages.append(rotMask) # Convert lists to NumPy arrays allTestImagesNP = np.array(allTestImages) maskTestImagesNP = np.array(maskTestImages) maskTestImagesNP = maskTestImagesNP.astype(int) print("Shapes of test Images and masks") print(allTestImagesNP.shape) print(maskTestImagesNP.shape) # Part 8: Save the processed data # Save processed training and test data as NumPy arrays print("Save the Train Data :") np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Melanoa-Images.npy", allImagesNP) # Save training images np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Melanoa-Masks.npy", maskImagesNP) # Save training masks print("Save the Test Data : ") np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Test-Melanoa-Images.npy", allTestImagesNP) # Save test images np.save("e:/temp/Unet-Test-Melanoa-Masks.npy", maskTestImagesNP) # Save test masks print("Finish save the Data ..........................") # Indicate the end of the saving processLink for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/901f79116c
U-Net in Keras: What You’re Training Here
U-Net is built for pixel-level prediction: it compresses the image to learn global context, then upsamples while merging high-resolution features through skip connections.
That “U” shape helps retain fine borders—exactly what you want for lesion boundaries.
In practice, U-Net quality is mostly driven by (1) clean masks, (2) consistent preprocessing, and (3) a loss/metric that matches segmentation (Dice/IoU style thinking).
Part 2 : The Unet Melanoma Detection model (Save it as “Step02Model.py”) :
This code defines a U-Net architecture using TensorFlow and Keras for image segmentation tasks.
It includes a convolutional block function (conv_block) for feature extraction, an encoder to downsample and extract spatial features, a bottleneck (bridge) for learning high-level features, and a decoder to upsample and combine features from corresponding encoder layers via skip connections.
The Melanoma Detection model outputs a single-channel mask with pixel values ranging from 0 to 1, suitable for binary segmentation tasks.
The build_model function constructs the full U-Net Melanoma Detection model based on a specified input shape.
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.layers import * from tensorflow.keras.models import Model # Convolutional block def conv_block(x, num_filters): """ This function defines a convolutional block consisting of two convolutional layers, each followed by batch normalization and ReLU activation. Parameters: x: Input tensor. num_filters: Number of filters for the convolutional layers. Returns: x: Output tensor after applying the convolutional block. """ x = Conv2D(num_filters, (3, 3), padding="same")(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation("relu")(x) x = Conv2D(num_filters, (3, 3), padding="same")(x) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation("relu")(x) return x # Build the U-Net model def build_model(shape): """ Builds a U-Net model for image segmentation. Parameters: shape: Tuple representing the shape of the input image (Height, Width, Channels). Returns: model: A compiled Keras Model object representing the U-Net architecture. """ num_filters = [64, 128, 256, 512] # Number of filters for each encoder block inputs = Input(shape) # Input layer skip_x = [] # List to store skip connections x = inputs # Encoder: Downsampling path for f in num_filters: x = conv_block(x, f) # Apply convolutional block skip_x.append(x) # Store skip connection x = MaxPool2D((2, 2))(x) # Downsample # Bridge: Bottleneck of the U-Net x = conv_block(x, 1024) # Prepare for the decoder num_filters.reverse() # Reverse the filter list for the decoder skip_x.reverse() # Reverse the skip connections # Decoder: Upsampling path for i, f in enumerate(num_filters): x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x) # Upsample xs = skip_x[i] # Retrieve the corresponding skip connection x = Concatenate()([x, xs]) # Concatenate skip connection x = conv_block(x, f) # Apply convolutional block # Output layer: Single-channel prediction with sigmoid activation (binary segmentation) x = Conv2D(1, (1, 1), padding="same")(x) x = Activation("sigmoid")(x) return Model(inputs, x)Link for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/901f79116c
Part 3 : Train the Melanoma Detection model :
This code implements the training pipeline for a U-Net Melanoma Detection model designed for melanoma segmentation.
It begins by loading preprocessed training and test data stored as NumPy arrays. The U-Net model is built using a separate script (Step02Model.py) with a predefined architecture.
The code configures hyperparameters like input shape, learning rate, batch size, and number of epochs. It employs the Adam optimizer and binary cross-entropy loss for training the model. Several callbacks, including ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, and EarlyStopping, are used to save the best model, adjust the learning rate dynamically, and stop training early if performance stops improving.
Finally, the Melanoma Detection model is trained using the loaded dataset, with training and validation metrics logged during each epoch to monitor the model’s progress. The best model is saved as a file for future use.
import numpy as np # Importing numpy for numerical operations # load the saved Numpy arrays (train and test data) print("Load the Train and Test Data :") # Load the training images and masks as Numpy arrays allImagesNP = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Melanoa-Images.npy") maskImagesNP = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Train-Melanoa-Masks.npy") # Load the test images and masks as Numpy arrays allTestImagesNP = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Test-Melanoa-Images.npy") maskTestImagesNP = np.load("e:/temp/Unet-Test-Melanoa-Masks.npy") # Print the shapes (dimensions) of the loaded data arrays print(allImagesNP.shape) print(maskImagesNP.shape) print(allTestImagesNP.shape) print(maskTestImagesNP.shape) Height = 128 # Set the height for the image size (used later in the model) Width = 128 # Set the width for the image size (used later in the model) # Importing necessary libraries for building and training the model import tensorflow as tf # TensorFlow for deep learning tasks from Step02Model import build_model # Import the custom model-building function from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping # Import useful callbacks # Define the shape of input images for the model (height, width, channels) shape = (128, 128, 3) lr = 1e-4 # Set the learning rate for the optimizer (smaller for fine-tuning) batch_size = 8 # Define the batch size for training epochs = 50 # Set the number of training epochs # Build the model using the custom function and defined input shape model = build_model(shape) # Print the summary of the model architecture print(model.summary()) # Set the optimizer to Adam with the specified learning rate opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr) # Compile the model with binary cross-entropy loss and accuracy metric model.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=opt, metrics=['accuracy']) # Calculate the number of steps per epoch for training (rounded up to avoid partial batches) stepsPerEpoch = np.ceil(len(allImagesNP) / batch_size) # Calculate the number of steps per validation epoch (rounded up) validationSteps = np.ceil(len(allTestImagesNP) / batch_size) # Define the path to save the best model during training best_model_file = "e:/temp/melanoma-Unet.h5" # Set up the callbacks to monitor training and improve performance callbacks = [ ModelCheckpoint(best_model_file, verbose=1, save_best_only=True), # Save the best model ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', patience=5, factor=0.1, verbose=1, min_lr=1e-7), # Reduce learning rate when validation loss plateaus EarlyStopping(monitor="val_accuracy", patience=20, verbose=1) # Stop training early if no improvement in validation accuracy ] # Start training the model using the training and validation data history = model.fit(allImagesNP, maskImagesNP, batch_size=batch_size, # Define batch size for training epochs=epochs, # Number of epochs for training verbose=1, # Display training progress validation_data=(allTestImagesNP, maskTestImagesNP), # Provide validation data steps_per_epoch=stepsPerEpoch, # Steps per epoch for training validation_steps=validationSteps, # Steps per epoch for validation shuffle=True, # Shuffle the data during training callbacks=callbacks) # Use the callbacks defined earlierLink for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/901f79116c

How to Evaluate the Model (Beyond “Looks Good”)
Visual overlays are a great first check, but add at least one quantitative signal (Dice or IoU) so you can compare improvements over time.
If Dice/IoU is low but visuals look okay, you may be thresholding incorrectly or resizing masks inconsistently at inference time.
If Dice/IoU is high on train but low on test, that’s often overfitting—reduce augmentation bias, add more variety, or simplify training.
Part 4 : Test the Melanoma Detection Model (inference) :
This code loads a pre-trained U-Net model for melanoma detection, processes a test image, and predicts a binary mask representing the presence of melanoma.
It resizes and normalizes the input image, then applies the model to predict the mask. The predicted mask is thresholded, resized, and displayed alongside the original image and the ground truth mask.
The results are saved as images, and the program waits for user input before closing the display windows.
import numpy as np # Importing numpy for numerical operations import tensorflow as tf # Importing TensorFlow for deep learning tasks import cv2 # Importing OpenCV for image processing tasks # Load the pre-trained model best_model_file = "e:/temp/melanoma-Unet.h5" # Define the file path for the saved model # Load the saved model from the specified file model = tf.keras.models.load_model(best_model_file) # Print the model architecture summary to understand its structure print(model.summary()) # Set the image dimensions (height and width) for input to the model Height = 128 Width = 128 # Define the test image file path imgTestPath = "E:/Data-sets/Melanoma/ISIC2018_Task1-2_Validation_Input/ISIC_0012643.jpg" # Read the image using OpenCV img = cv2.imread(imgTestPath) # Resize the image to match the model's expected input size img2 = cv2.resize(img, (Width, Height)) # Normalize the image by scaling the pixel values to the range [0, 1] img2 = img2 / 255.0 # Add a new dimension to the image to match the input shape expected by the model (batch size, height, width, channels) imgForModel = np.expand_dims(img2, axis=0) # Print the shape of the image after resizing and preprocessing print(img2.shape) # Print the shape of the image after adding the batch dimension print(imgForModel.shape) # Make a prediction using the model on the preprocessed image p = model.predict(imgForModel) # Extract the predicted mask (first element from the prediction result) resultMask = p[0] # Print the shape of the predicted mask print("Result mask : ") print(resultMask.shape) # Since this is a binary classification task, apply a threshold to the predicted mask # Any pixel value above 0.5 will be set to 255 (White) # Any pixel value below or equal to 0.5 will be set to 0 (Black) resultMask[resultMask <= 0.5] = 0 resultMask[resultMask > 0.5] = 255 # Resize the original image and the predicted mask to a smaller size for display scale_precent = 25 # Define the percentage to scale the image and mask width = int(img.shape[1] * scale_precent / 100) # Calculate the new width height = int(img.shape[0] * scale_precent / 100) # Calculate the new height dim = (width, height) # Define the new dimensions # Resize the original image to the new dimensions img = cv2.resize(img, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # Resize the predicted mask to the new dimensions mask = cv2.resize(resultMask, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # Load the ground truth mask (real mask) for comparison trueMaskFile = "E:/Data-sets/Melanoma/ISIC2018_Task2_Validation_GroundTruth/ISIC_0012643_attribute_pigment_network.png" # Read the true mask image (the ground truth) trueMask = cv2.imread(trueMaskFile, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # Resize the true mask to the new dimensions trueMask = cv2.resize(trueMask, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # Show the original image, predicted mask, and real mask in separate windows cv2.imshow("First image", img) cv2.imshow("Predicted Mask", mask) cv2.imshow("Real mask", trueMask) # Save the predicted mask and the original image as separate files cv2.imwrite("e:/temp/predicted.png", mask) cv2.imwrite("e:/temp/img.png", img) # Wait for a key press before closing the windows cv2.waitKey(0)Link for the full code : https://ko-fi.com/s/901f79116c
The result (Medical Melanoma Detection) :

Common Failure Modes (and quick fixes)
If the model predicts “all background,” check: mask binarization, class imbalance, and whether masks load correctly (not inverted / not all zeros).
If predictions are noisy, check: learning rate, augmentation severity, and whether your input normalization matches training vs inference.
If inference masks are shifted, it’s usually a resize/shape mismatch—ensure the same width/height logic is used consistently throughout the pipeline.
Connect :
☕ Buy me a coffee — https://ko-fi.com/eranfeit
🖥️ Email : feitgemel@gmail.com
🤝 Fiverr : https://www.fiverr.com/s/mB3Pbb
Planning a trip and want ideas you can copy fast?
Here are three detailed guides from our travels:
• 5-Day Ireland Itinerary: Cliffs, Castles, Pubs & Wild Atlantic Views
https://eranfeit.net/unforgettable-trip-to-ireland-full-itinerary/
• My Kraków Travel Guide: Best Places to Eat, Stay & Explore
https://eranfeit.net/my-krakow-travel-guide-best-places-to-eat-stay-explore/
• Northern Greece: Athens, Meteora, Tzoumerka, Ioannina & Nafpaktos (7 Days)
https://eranfeit.net/my-amazing-trip-to-greece/
Each guide includes maps, practical tips, and family-friendly stops—so you can plan in minutes, not hours.
Enjoy,
Eran
